
使用 Playwright JavaScript 进行 API 测试
· 2,642 词 · 14 分钟 读完 playwright进阶 翻译
首先,让我们从 API 测试的基础知识开始。我们将探讨 API 测试中使用的基本方法,然后深入探讨设计有效 API 测试用例的最佳实践。

使用 HTTP 方法进行 API 测试
- GET: 用于获取数据。
示例:获取 ID 为'1'的书籍的价格、作者姓名和书籍类别。 - POST: 用于创建新资源。
示例:通过提供书籍名称和 ID 等详细信息来创建一本新书。 - PUT: 用于通过完全替换数据来更新现有资源的所有字段。
示例:更新 ID 为'1'的书籍的价格、作者姓名和书籍类别。 - PATCH: 用于更新现有资源的特定字段,而不替换整个数据。
示例:仅更新 ID 为'1'的书籍的价格。 - DELETE: 用于删除特定资源。
示例:删除 ID 为'1'的书籍的所有详细信息。
现在,激动人心的部分来了!!Playwright JavaScript 如何发起请求。
项目设置:
假设您已经在本地环境中安装了 Node.js,您可以通过以下命令安装 Playwright。
npm init @playwright/test
如何在 Playwright 中发起 API 请求:
使用 直接使用 HTTP 方法的请求:
const { test, expect } = require("@playwright/test");
// 使用不同 HTTP 方法的示例
test("不同的 HTTP 方法", async ({ request }) => {
// GET 请求
const getResponse = await request.get(url, {
params: { id: 123 }, // 这些会成为查询参数
});
// POST 请求
const postResponse = await request.post(url, {
data: { name: "test" }, // 请求体
});
// PUT 请求
const putResponse = await request.put(url, {
data: { name: "updated" },
});
// PATCH 请求
const patchResponse = await request.patch(url, {
data: { status: "active" },
});
// DELETE 请求
const deleteResponse = await request.delete(url);
// HEAD 请求
const headResponse = await request.head(url);
});
使用 newContext:
// 创建一个具有共享设置的上下文
const apiContext = await request.newContext({
baseURL: "https://api.example.com",
extraHTTPHeaders: {
Authorization: "Bearer token123",
Accept: "application/json",
},
});
// 使用该上下文进行多个请求
const usersResponse = await apiContext.get("/users");
const postsResponse = await apiContext.get("/posts");
使用 newContext 的主要好处:
- 可重用的配置:
// 一次性设置,随处使用
const apiContext = await request.newContext({
baseURL: "https://api.example.com",
extraHTTPHeaders: {
Authorization: "Bearer token123",
Accept: "application/json",
},
timeout: 30000,
});
// 所有这些请求都使用相同的配置
await apiContext.get("/users");
await apiContext.post("/orders");
await apiContext.put("/profile");
- 灵活性:当您在同一测试中需要不同的配置时
test("测试多个 API", async ({ playwright }) => {
// 用于 API 版本 1 的上下文
const v1Context = await playwright.request.newContext({
baseURL: "https://api.v1.example.com",
extraHTTPHeaders: { "API-Version": "1.0" },
});
// 用于 API 版本 2 的上下文
const v2Context = await playwright.request.newContext({
baseURL: "https://api.v2.example.com",
extraHTTPHeaders: { "API-Version": "2.0" },
});
// 在同一测试中使用两个上下文
const v1Response = await v1Context.get("/data");
const v2Response = await v2Context.get("/data");
// 清理
await v1Context.dispose();
await v2Context.dispose();
});
- 会话管理:
test("详细的会话处理示例", async ({ request }) => {
const apiContext = await request.newContext();
// 1. 初始尝试访问受保护的路由(应该失败)
const initialResponse = await apiContext.get("/protected-data");
expect(initialResponse.status()).toBe(401); // 未授权
// 2. 发起登录请求
const loginResponse = await apiContext.post("/login", {
data: {
username: "testuser",
password: "testpass",
},
});
// 3. 服务器通常会返回类似的内容:
// Set-Cookie: sessionId=abc123; Path=/; HttpOnly
// apiContext 会自动捕获这些内容
// 如果需要,您可以检查 cookies
console.log("响应头:", loginResponse.headers());
// 4. 下一个请求会自动包含 cookie
const protectedResponse = await apiContext.get("/protected-data");
expect(protectedResponse.ok()).toBeTruthy(); // 现在它可以工作了!
// 5. 您可以发起多个请求,所有请求共享同一个会话
const profileResponse = await apiContext.get("/profile");
const ordersResponse = await apiContext.get("/orders");
const settingsResponse = await apiContext.get("/settings");
// 所有这些请求都自动包含了会话 cookie
});
何时使用直接请求和 newContext:
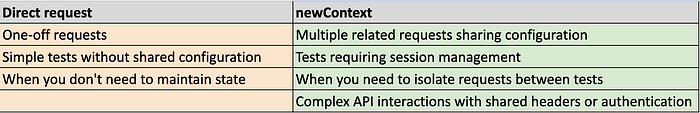
然而,如果您不需要在测试用例之间共享会话,并且更倾向于为每个测试使用全新的会话,我建议使用
test.use()进行全局设置的直接请求 API,例如配置 API 头信息。test.use()方法会自动处理清理工作,默认情况下确保测试隔离,并通过一致的配置使测试更易于维护。然而,当使用request.newContext时,它会跨测试维护会话状态(例如 cookies 和 localStorage),直到您显式调用dispose()函数。
使用 test.use() 的示例代码:
test.describe("使用 test.use 进行测试", () => {
test.use({
extraHTTPHeaders: {
Authorization: "Bearer token",
},
});
test("第一次登录", async ({ request }) => {
const loginResponse = await request.post("/api/login", {
data: { username: "user1", password: "pass1" },
});
// 这会创建一个 cookie 会话
const profileResponse = await request.get("/api/profile");
// 此请求使用登录后的 cookie
});
test("第二次登录", async ({ request }) => {
// 此测试完全重新开始!
// 前一个测试的 cookies 不会被携带过来
const profileResponse = await request.get("/api/profile");
// 这会失败,因为我们没有会话
});
});
使用 newContext 的示例代码:
test.describe("使用 request.newContext 进行测试", () => {
let context;
test.beforeAll(async ({ request }) => {
context = await request.newContext({
extraHTTPHeaders: {
Authorization: "Bearer token",
},
});
});
test("第一次登录", async () => {
const loginResponse = await context.post("/api/login", {
data: { username: "user1", password: "pass1" },
});
// 这会创建一个 cookie 会话
const profileResponse = await context.get("/api/profile");
// 此请求使用登录后的 cookie
});
test("第二次登录", async () => {
// 此测试将能够访问前一个测试的 cookies!
const profileResponse = await context.get("/api/profile");
// 这会成功,因为会话仍然有效
});
test.afterAll(async () => {
await context.dispose(); // 清理资源
});
});
让我们看看 Playwright 请求选项的完整结构:
test("演示所有请求选项", async ({ request }) => {
const response = await request.post("https://api.example.com/endpoint", {
// 1. 头信息
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json",
Authorization: "Bearer token123",
"Custom-Header": "value",
},
// 2. 请求体 - 可以作为 'data' 发送
data: {
name: "Test User",
email: "test@example.com",
},
// 3. 查询参数
params: {
page: 1,
limit: 10,
},
// 4. 超时设置
timeout: 30000, // 30 秒
// 5. 表单数据 (multipart/form-data)
multipart: {
file: {
name: "test.txt",
mimeType: "text/plain",
buffer: Buffer.from("content"),
},
field: "value",
},
// 6. 忽略 HTTPS 错误
ignoreHTTPSErrors: true,
// 7. 最大重定向次数
maxRedirects: 5,
// 8. 在非 200 状态码时失败
failOnStatusCode: true,
// 9. 重试失败的请求
maxRetries: 3,
});
});
关于 Playwright 请求 API 的关键知识点:
常见选项:
data: 请求体(自动为 JSON 字符串化)headers: 请求头params: 查询参数timeout: 请求超时时间(毫秒)failOnStatusCode: 是否在非 200 响应时抛出错误ignoreHTTPSErrors: 是否忽略 HTTPS 错误form: 用于表单提交multipart: 用于文件上传
此外,如果您想对与重定向端点相关的 API 进行安全测试,可以使用 followRedirects: false 选项。
test("未认证访问时应重定向到登录页面", async () => {
// 创建一个没有任何默认头信息的新上下文
const cleanContext = await request.newContext();
try {
// 仅使用重定向头信息发起请求,并确保这是一个全新的请求
const response = await cleanContext.get(`${BASE_URL}/admin/inventory`, {
headers: {
Accept: "application/json",
"X-Handle-Redirect": "true",
},
followRedirects: false,
maxRedirects: 0,
});
const responseHeaders = await response.headers();
const responseStatus = response.status();
// 验证重定向
expect(responseStatus).toBe(302);
expect(responseHeaders["location"]).toBe("/auth/login");
// 手动跟随重定向
if (responseHeaders["location"]) {
const loginResponse = await cleanContext.get(
`${BASE_URL}${responseHeaders["location"]}`,
{
headers: { Accept: "application/json" },
}
);
expect(loginResponse.status()).toBe(200);
const loginData = await loginResponse.json();
expect(loginData.message).toBe("请登录以继续");
expect(loginData.redirected).toBe(true);
}
} finally {
await cleanContext.dispose();
}
});
如果没有 followRedirects: false,如果服务器返回 302 重定向,Playwright 会自动跟随重定向到 /auth/login,并且 response 将来自登录页面(状态码 200)。我们将无法验证是否发生了重定向。
API 响应中的常见检查:
// 使用此上下文发起请求
const response = await apiContext.get("/users");
// 重要的响应检查:
// 1. 状态码检查
expect(response.status()).toBe(200);
// 2. Content-Type 头信息检查
const headers = response.headers();
expect(headers["content-type"]).toContain("application/json");
expect(headers["cache-control"]).toBeDefined();
// 3. 响应结构检查
const data = await response.json();
expect(data).toHaveProperty("users");
// 模式验证
expect(body).toMatchObject({
id: expect.any(Number),
name: expect.any(String),
createdAt: expect.any(String),
});
// 4. 响应时间检查(性能)
const timing = await response.timing();
expect(timing.responseEnd).toBeLessThan(2000); // 2 秒
// 5. 错误处理
const errorResponse = await request.get("https://api.example.com/non-existent");
if (!errorResponse.ok()) {
const errorBody = await errorResponse.json();
expect(errorBody).toHaveProperty("error");
expect(errorBody.error).toHaveProperty("message");
}
要在 Playwright 中发起 API 请求,重要的是要理解 JavaScript 概念,如 async/await、Promise.all()、Promise.race()、Promise.allSettled() 和 Promise 链式调用。以下是每种类型在 API 请求中的使用示例:
Promise.all()- 当您需要并行发起多个请求并且所有请求都必须成功时使用:
test("Promise.all 示例", async ({ request }) => {
// 当您需要所有请求都成功时使用
try {
const [usersResponse, postsResponse, commentsResponse] = await Promise.all([
request.get("https://api.example.com/users"),
request.get("https://api.example.com/posts"),
request.get("https://api.example.com/comments"),
]);
// 如果任何一个请求失败,整个 Promise.all 都会失败
const users = await usersResponse.json();
const posts = await postsResponse.json();
const comments = await commentsResponse.json();
// 现在您可以处理所有数据
expect(users.length).toBeGreaterThan(0);
expect(posts.length).toBeGreaterThan(0);
expect(comments.length).toBeGreaterThan(0);
} catch (error) {
console.error("其中一个请求失败:", error);
}
});
Promise.race()- 当您想要获取最先完成的请求的结果时使用:
test("Promise.race 示例", async ({ request }) => {
// 用于测试故障转移场景或实现超时
const timeoutPromise = new Promise((_, reject) =>
setTimeout(() => reject(new Error("请求超时")), 5000)
);
try {
// 在实际请求和超时之间进行竞争
const response = await Promise.race([
request.get("https://api.example.com/data"),
timeoutPromise,
]);
const data = await response.json();
expect(data).toBeDefined();
} catch (error) {
console.error("请求超时或失败:", error);
}
});
Promise.allSettled()- 当您想知道所有请求的结果,无论成功还是失败时使用:
当您发起普通请求时,如果任何请求失败,它会立即抛出错误。
test("普通请求 vs Promise.allSettled", async ({ request }) => {
// 普通请求方法
try {
// 如果其中任何一个失败,代码将在该点停止执行
const response1 = await request.post("https://api.example.com/orders", {
data: { id: "001", item: "有效项目" },
});
const response2 = await request.post("https://api.example.com/orders", {
data: { id: "002", item: "" }, // 无效 - 项目为空
});
const response3 = await request.post("https://api.example.com/orders", {
data: { id: "003", item: "另一个有效项目" },
});
// 如果 response2 失败,此代码不会运行
console.log("所有订单已创建");
} catch (error) {
console.log("发生错误,停止所有操作");
}
// Promise.allSettled 方法
const orderRequests = [
{ id: "001", item: "有效项目" },
{ id: "002", item: "" }, // 无效 - 项目为空
{ id: "003", item: "另一个有效项目" },
];
const results = await Promise.allSettled(
orderRequests.map((order) =>
request.post("https://api.example.com/orders", {
data: order,
})
)
);
// 无论是否有失败,此代码都会运行
// 您可以看到哪些订单成功,哪些失败
const summary = {
successful: [],
failed: [],
};
for (let i = 0; i < results.length; i++) {
const result = results[i];
const order = orderRequests[i];
if (result.status === "fulfilled" && result.value.ok()) {
summary.successful.push({
id: order.id,
response: await result.value.json(),
});
} else {
summary.failed.push({
id: order.id,
error:
result.status === "rejected"
? result.reason
: await result.value.json(),
});
}
}
console.log("总结:", summary);
// 这可能会显示:
// 总结: {
// successful: [
// { id: '001', response: {...} },
// { id: '003', response: {...} }
// ],
// failed: [
// { id: '002', error: '项目不能为空' }
// ]
// }
// 您仍然可以处理成功的订单
expect(summary.successful.length).toBe(2);
expect(summary.failed.length).toBe(1);
});
关键区别:

- Promise 链式调用 - 当操作需要按顺序进行并且依赖于先前的结果时使用:
test("Promise 链式调用示例", async ({ request }) => {
// 第一种方法 - 使用 .then()
request
.post("https://api.example.com/users", {
data: { name: "John" },
})
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((user) =>
request.post(`https://api.example.com/users/${user.id}/orders`, {
data: { product: "item1" },
})
)
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((order) => {
expect(order.status).toBe("created");
})
.catch((error) => console.error("错误:", error));
// 第二种方法 - 使用 async/await(更易读)
try {
const userResponse = await request.post("https://api.example.com/users", {
data: { name: "John" },
});
const user = await userResponse.json();
const orderResponse = await request.post(
`https://api.example.com/users/${user.id}/orders`,
{
data: { product: "item1" },
}
);
const order = await orderResponse.json();
expect(order.status).toBe("created");
} catch (error) {
console.error("错误:", error);
}
});
感谢阅读,希望您觉得这篇文章有帮助。
如果您想了解更多关于使用 Playwright 进行 API 测试的最佳实践,我建议您阅读这篇博客。